Briefly Describe the Thévenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits.
Norton Current Thevenin Voltage Equivalent Impedance 1058V. In the final stage that is in the equivalent circuit the current is placed in parallel to the internal resistance in Nortons Theorem whereas in Thevenins Theorem the equivalent voltage source is placed in series with the internal resistance.
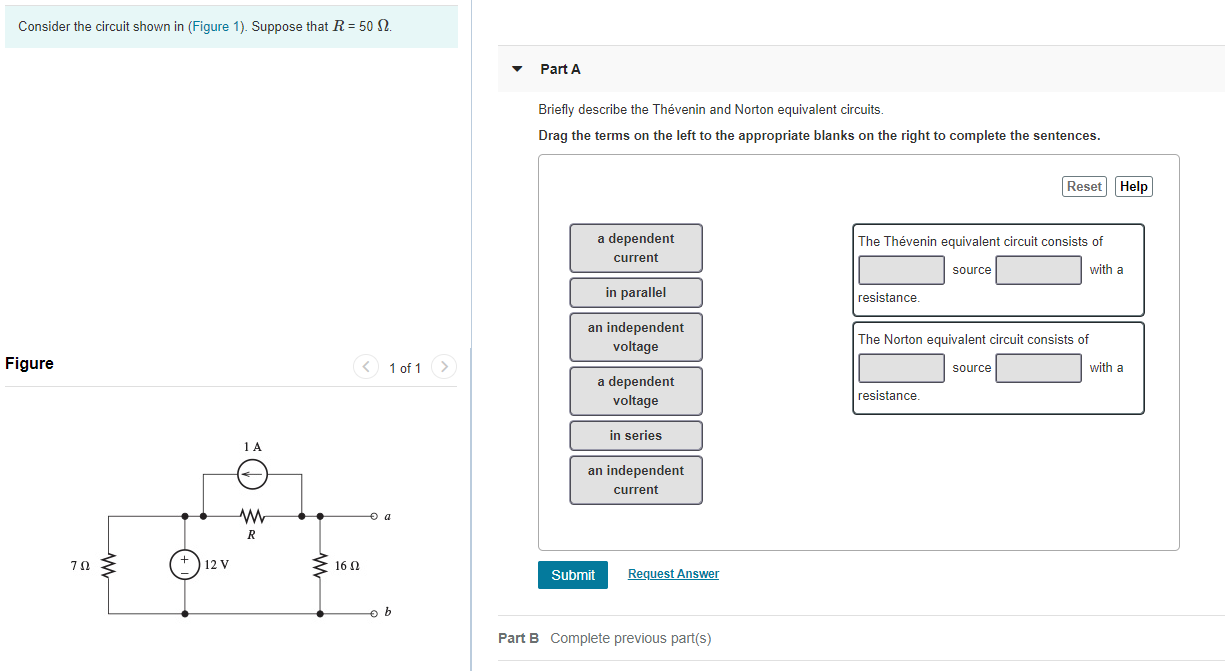
Solved Consider The Circuit Shown In Figure 1 Suppose Chegg Com
The determination of internal resistance of the source network is identical in both the theorems.

. One final important note is that Ohms law applies to the equivalent circuits. Review Briefly describe the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits. Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences.
L5 5 5 5 5 5 6 P. The main difference between Thevenins theorem and Nortons theorem is that Thevenins theorem provides an equivalent voltage source and an equivalent series resistance while Nortons theorem provides an equivalent Current source and an equivalent parallel resistance. P YRF L5 5.
Nortons Theorem is the replacement of a large part of a circuit often a complicated part by a very simple equivalent. The Norton equivalent resistance is the resistance between these. Then the result is used to model and simulate how the circuit will behave when different components are used to close the circuit path.
Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1. Suppose that R 22 12. The Thevenins equivalent circuit is usually calculated for an open circuit.
Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1. Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang course materials for. V T I N R N.
Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to. Note that R 3 is shorted out. From the perspective of outside terminals any series combination of an ideal voltage source plus resistor ie.
Start with a current divider. 9V Th v oc 432 V Find i sc. The Norton equivalent circuit consists of source with a resistance.
Reset Help a dependent voltage The Thévenin equivalent circuit consists of a dependent voltage source in series with a resistance. Thevenins Example summary 1 The graph shown in the right hand side gives the final result for Thevenins theory. The last time I used this was yesterday and I used both and I regularly use both.
A Thevenin equivalent circuit can be transformed into a parallel combination of an ideal current source plus resistor called a Norton equivalent circuit. Thevenins Theorem and Nortons Theorem both are important DC network analysis techniques or theorem. And it is clear that every circuit have both their Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits for a terminal or load.
The short-circuit current available from these two terminals is the Norton current. Compared with original circuit it looks a lot easier to further analyze. Add the load resistor in parallel with the above circuit and apply current division rule to find the load current.
R T R N. The process of exchanging one for the other is called. Nortons Theorem states that.
Part B Reset Help in series in parallel an independent current a dependent voltage an independent voltage a dependent current The Thévenin equivalent circuit consists of source with a resistance. Now draw Nortons equivalent circuit with nortons current source in parallel with thevenins resistance. 2 Generally speaking out of the two ways in findng equivalent resistor.
Then one subcircuit can be exchanged for the other in any circuit problem. 1011 with a source an Nov 04 2021 0215 PM. This theorem is very useful because of the conversion of real life components to ideal components.
The Nortons. Port resistance of network seen from port s s set to 0. Use a current divider again.
These two circuits equations are the same if the following is true. Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalents of the circuit at right with the port as shown. Suppose that R-34 O.
P N. R 1 R 2 I S i sc LVF 5 5 5 6. V oc 6 k.
So a much quicker way to calculate the Norton current in the example above would have been to use Ohms Law. Equivalent network RTH vTH open circuit voltage at terminal pair aka. 1 of 2 272018 1232 PM.
P 282 Briefly describe the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits. Any two terminals of a network of any number of resistors current sources andor voltage sources can be reduced to one current source in parallel with one resistor. Basically Norton converts a bunch of resistors attached to a voltage source into a current source in parallel with a single equivalent resistor and Thevenin does the same except it converts to a voltage source in series with a single equivalent resistor.
B is more useful in the. A is more suitable for graph containing denpendent source. Identify The Load Resistance.
Any linear electric network or complex circuit with current and. ResetHelp in series The Thévenin equivalent circuit consists of Figure. 24 mA 3 k.
It enables us to make rapid calculations of the voltage current and power which the original circuit is able to deliver to a load. Solution - in thevenin equivalent the thevenin voltage source is connected in series with the loadin norton equivalent circuitthe current source is. The new circuit replaced by a single constant current generator in parallel with a single resistor.
As with Thevenins Theorem everything in the original circuit except the load resistance has been reduced to an equivalent circuit that is simpler to analyze. Also similar to Thevenins Theorem are the steps used in Nortons Theorem to calculate the Norton source current I Norton and Norton resistance R Norton. Since the Thevenin and Norton subcircutis are equivalent if R T R N and V T I N R N.
The load current is calculated as So the load is calculated as 4 Amperes as shown in the above figure. Norton equivalent TH TH N R V I RTH RN IN J.

Norton And Thevenin Equivalent Circuits Derived By The Rational Download Scientific Diagram
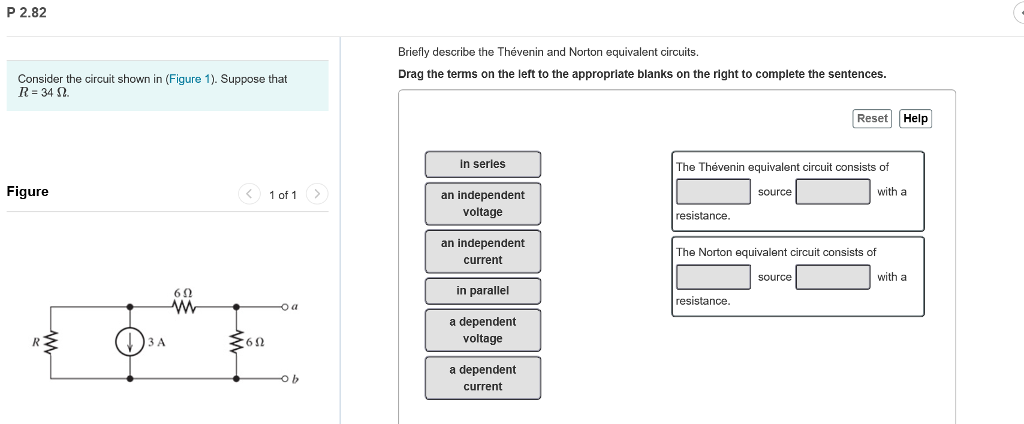
Solved P 2 82 Briefly Describe The Thevenin And Norton Chegg Com

No comments for "Briefly Describe the Thévenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits."
Post a Comment